Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The ability of soils to release water so that it flows through the topsoil into
the subsoil, and eventually to aquifers, is called _____.
A. | drainage | B. | weathering | C. | filtration | D. | aggregation |
|
|
|
2.
|
What is the largest soil particle?
A. | Silt | B. | Gravel | C. | Sand | D. | Clay |
|
|
|
3.
|
What is parent material?
A. | Hard rock that has not weathered and cannot be excavated | B. | Geological material
from which soil is formed | C. | Soil that has a pH above 7 | D. | Soil that has a pH
below 7 |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which soil horizon is located just immediately below the vegetation?
A. | A-horizon | B. | B-horizon | C. | C-horizon | D. | O-horizon |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which soil horizon contains the most organic matter in soil?
A. | A-horizon | B. | B-horizon | C. | O-horizon | D. | R-horizon |
|
|
|
6.
|
The parent material is located in which soil horizon?
A. | O-horizon | B. | B-horizon | C. | C-horizon | D. | R-horizon |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which structural form of soil is shown in this image? 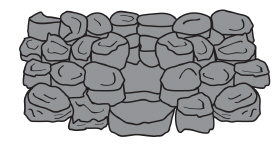 A. | Granular | B. | Blocky | C. | Platey | D. | Columnar |
|
|
|
8.
|
Class _____ land has very gentle slopes, slightly shallower soils, and drainage
issues that can generally be corrected with grassed waterways or subsurface tile drainage.
|
|
|
9.
|
Which class of land is very steep and is primarily suitable for grazing,
woodlots, and wildlife cover?
A. | Class III | B. | Class IV | C. | Class
V | D. | Class VII |
|
|
|
10.
|
In which season do deer species rut?
A. | Autumn | B. | Spring | C. | Summer | D. | Winter |
|
|
|
11.
|
This photo shows an example of a(n) _____ forest.  A. | deciduous | B. | coniferous | C. | dehiscent | D. | indehiscent |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which tree is an example of a deciduous tree?
A. | Larch | B. | Spruce | C. | Fir | D. | Birch |
|
|
|
13.
|
Trees reproduce sexually by _____.
A. | producing seeds | B. | growing leaves or needles | C. | shedding their
bark | D. | extending their roots |
|
|
|
14.
|
A compound leaf is a leaf that _____.
A. | produces seeds in cones | B. | starts out as a leaf but is later replaced by a
needle | C. | is exceptionally rigid | D. | is made up of multiple
leaflets |
|
|
|
15.
|
Trees cut for lumber are generally cut into _____ lengths.
|
|
|
16.
|
The overall reduction in the number of trees in an area of the forest is called
_____.
A. | culling | B. | coppicing | C. | girdling | D. | thinning |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is a Biltmore stick commonly used for?
A. | Measuring the harvestable height of a tree | B. | Clearing slash from
the forest floor | C. | Marking trees for culling | D. | Marking the ground to measure the level of pond
succession |
|
|
|
18.
|
Using the table below, determine the volume of a tree with a DBH of 34”
(0.86 m) that contains four 16’ (4.9 m) logs.  A. | 506 board feet | B. | 1385 board feet | C. | 1487 board
feet | D. | 1610 board feet |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which practice involves removing all trees from a given area?
A. | Shelterwood harvesting | B. | Seed tree harvesting | C. | Strip-cutting | D. | Clear-cutting |
|
|
|
20.
|
This photograph shows an image of which invasive plant pest?  A. | Cogon grass | B. | Chinese tallow | C. | Kudzu | D. | Japanese
honeysuckle |
|
|
|
21.
|
What is the largest soil particle?
A. | Silt | B. | Gravel | C. | Sand | D. | Clay |
|
|
|
22.
|
A habitat is...
A. | Any landscape that provides some of the needs of a species. | C. | The environment in
which the specific needs of a species are met. | B. | Any place where we find vegetation such as
trees or grass. | D. | All of the
above. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Why does habitat loss represent one of the greatest causes of extinction?
A. | Living organisms have evolved over millions of years to have highly specific needs
that are met only by their specific habitats. | C. | Without a habitat, a species cannot
live under natural conditions. | B. | If a habitat is changed, it can no longer
provide the conditions necessary for species to live. | D. | All of the
above. |
|
|
|
24.
|
The maximum population that a habitat can sustainably support is called
a…
A. | Carrying Capacity | C. | Ecosystem | B. | Community | D. | Niche |
|
|
|
25.
|
The interaction of living and non-living species in an area is
called…
A. | Carrying Capacity | C. | Ecosystem | B. | Community | D. | Niche |
|
|
|
26.
|
The specific role a species plays in its habitat is called…
A. | Carrying Capacity | C. | Ecosystem | B. | Community | D. | Niche |
|
|
|
27.
|
The interactions of living species in a habitat is a…
A. | Carrying Capacity | C. | Ecosystem | B. | Community | D. | Niche |
|
|
|
28.
|
This niche is when species interact to the benefit of all involved.
A. | Competition | D. | Symbiosis | B. | Predation/Parasitism | E. | Commensalism | C. | Mutualism |
|
|
|
29.
|
This niche is when two species struggle to acquire the same resource.
A. | Competition | D. | Symbiosis | B. | Predation/Parasitism | E. | Commensalism | C. | Mutualism |
|
|
|
30.
|
This niche is when one species gains resources at the expense of another
species.
A. | Competition | D. | Symbiosis | B. | Predation/Parasitism | E. | Commensalism | C. | Mutualism |
|
|
|
31.
|
This niche is when one species benefits without affecting another
species.
A. | Competition | D. | Symbiosis | B. | Predation/Parasitism | E. | Commensalism | C. | Mutualism |
|
|
|
32.
|
This niche is where two species cooperate to the extent that they physically
cannot survive without each other.
A. | Competition | D. | Symbiosis | B. | Predation/Parasitism | E. | Commensalism | C. | Mutualism |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following best describes amensalism?
A. | When one species benefits another species without benefiting itself. | C. | When one species
benefits another species without harming itself. | B. | When one species harms another species without
benefiting itself. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following best summarizes the Competition Exclusion
Principle?
A. | If two species occupy the same niche at the same time, they will cooperate to use the
resources. | C. | If two species occupy the same niche at the same time, both will go
extinct. | B. | If two species occupy the same niche at the same time, one species will eliminate the
other over time. | D. | All of the
above are accurate summaries. |
|
|
|
35.
|
A species with a very narrow niche is called a…
A. | Habitat generalist | C. | Predator | B. | Habitat specialist | D. | Threatened or endangered
species |
|
|
|
36.
|
As habitats become ________________ , the impact of the Competitive Exclusion
Principle ________________ .
A. | Smaller; Increases | C. | Larger; Increases | B. | Smaller;
Decreases |
|
|
|
37.
|
How do invasive species affect the Competitive Exclusion Principle?
A. | Invasive species reduce competition within a niche, providing more ecosystem services
to native species. | C. | Invasive species increase the competition within a niche, making it harder to acquire
resources. | B. | Invasive species expand the number of niches in an ecosystem. | D. | All of the
above. |
|
|
|
38.
|
The process in which a habitat undergoes natural, slow change is
called…
A. | Succession | C. | Resilience | B. | Disturbance |
|
|
|
39.
|
The ability of a habitat to overcome threats and return to a normal state is
known as…
A. | Succession | C. | Resilience | B. | Disurbance |
|
|
|
40.
|
How do human-caused disturbances differ from natural disturbances?
A. | They do not differ; both cause extensive damage and threaten
biodiversity | C. | Human disturbances occur on a much smaller scale than natural
disturbances | B. | Natural disturbances tend to be rapid and temporary; human disturbances tend to have
a longer impact. | D. | Human
disturbances are rare while natural disturbances occur much more
often. |
|
|
|
41.
|
The _____________ the biodiversity of a habitat, the_____________ the resilience
of that habitat.
A. | Greater; Greater | C. | Lower; Greater | B. | Greater; Lower |
|
|
|
42.
|
What is habitat fragmentation?
A. | When a habitat experiences a selective harvest of timber. | C. | When a habitat is
broken into multiple smaller habitats that are isolated from each other. | B. | When a habitat
experiences a disturbance such as pollution or invasive species. | D. | All of the
above. |
|
|
|
43.
|
The ______________ the size of the habitat, and the ______________ the
biodiversity, the ______________ the habitat will be.
A. | Greater; Lower; Healthier | C. | Greater; Higher;
Healthier | B. | Smaller; Lower; Healthier |
|
|
|
44.
|
The main causes of habitat fragmentation include…
A. | Succession, natural disturbances, pollution, and hunting. | C. | Human development,
succession, natural disturbances, and deforestation. | B. | Road building, succession, natural
disturbances, and conversion. | D. | Human development, road building, deforestation, and
conversion. |
|
|
|
45.
|
Which of the following is NOT an outcome of fragmentation?
A. | Decreased populations due to lowered carrying capacities. Inbreeding and losses of
genetic diversity. | C. | Loss of specialist species with narrow niches. | B. | Increased predation,
parasitism, and invasive species. | D. | Increased species diversity due to evolution resulting from new selection
pressures. |
|
|
|
46.
|
What is the difference between patchiness and edge?
A. | Patchiness is the amount of border a habitat has while edge is how broken up a
habitat is. | C. | Patchiness is another word for fragmentation; edge is a result of the
fragmentation. | B. | Edge is the amount of border a habitat has while patchiness is how broken up a
habitat is. | D. | Edge is another
word for fragmentation; patchiness is a result of the fragmentation. |
|
|
|
47.
|
Which is not one of the 7 glands found on the body of a white-tailed
deer?
A. | Post-orbital gland | C. | Preputial gland | B. | Forehead gland | D. | Tarsal gland |
|
|
|
48.
|
Antlers are different than horns in all of the following ways except?
A. | Antlers shed and regrown annually | C. | Antlers grow from the
base. | B. | Antlers are made of calcified “true” bone. | D. | Antlers are used during sparring and fighting
to establish hierarchy. |
|
|
|
49.
|
Which sensory organ is referred to as the whitetail’s “sixth
sense”?
A. | Obamasum | C. | Vomeronasal organ | B. | Interdigital gland | D. | Nasal gland |
|
|
|
50.
|
White-tailed deer are classified as ruminants due to:
A. | Having a single four-chambered stomach | C. | Having four stomachs that do not
differ in function | B. | Having four stomachs that each provide a
different function |
|
|
|
51.
|
White-tailed deer gestation period is:
A. | 160-165 days | C. | 185-195 days | B. | 170-175 days | D. | 195-200 days |
|
|
|
52.
|
Which of the following information can be gained from a trail-camera
survey?
A. | Deer density | D. | Buck-to-doe ratio | B. | Idea of buck age-structure | E. | All answers are correct | C. | Fawn recruitment
rate |
|
|
|
53.
|
Quality Deer Management is define by:
A. | The approach where young bucks are protected from harvest, combined with an adequate
harvest of female deer to produce healthy deer herds in balance with existing habitat
conditions. | C. | The approach where any antlered buck is harvested, regardless of age or antler
quality, and few does are harvested. | B. | The approach where only fully mature bucks with
high-scoring antlers are harvested (with the exception of low-scoring middle-aged bucks) and does are
aggressively harvested to maintain low deer density and optimum nutrition for the remaining
animals. | D. | No answers are
correct. |
|
|
|
54.
|
What is the age of this deer? 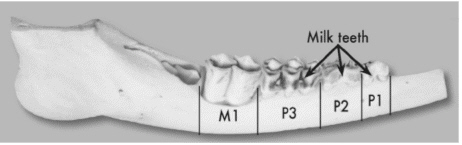 A. | Fawn | C. | 2.5 years old | B. | 1.5 years old |
|
|
|
55.
|
What is the age of this deer? 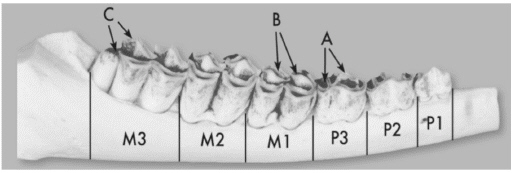 A. | Fawn | C. | 2.5 years old | B. | 1.5 years old |
|
|
|
56.
|
What is the age of this deer? 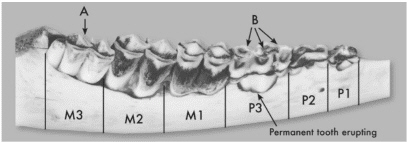 A. | Fawn | C. | 2.5 years old | B. | 1.5 years old |
|
|
|
57.
|
What is the system called that groups soils with similar limitations and
classifies them according to the best possible use?
A. | Land Factor | C. | Land Capability Class | B. | Land
Form | D. | Land Use
Class |
|
|
|
58.
|
The _____ number, the less suitable the land is for crop production.
A. | Higher | C. | Even | B. | Lower | D. | Odd |
|
|
|
59.
|
The most common limiting factor for classifying land as cultivatable
is...
A. | Drainage | C. | Erosion | B. | Topsoil Thickness | D. | Slope |
|
|
|
60.
|
Read the diameter tape below: 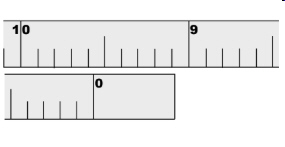
|
|
|
61.
|
What is the total height of the tree below? 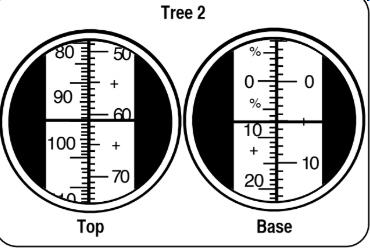
|
|
|
62.
|
An accident is
A. | Sudden or unintentional event that causes injury | C. | a substance used to stop pain or
itching. | B. | What happens when you wet the bed. | D. | loss of salt resulting in muscular pains &
spasms. |
|
|
|
63.
|
A way to prevent heat being an environmental hazard is to
A. | wear proper clothing | C. | pace yourself | B. | know the signs of heat
exhaustion | D. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
64.
|
Insects are generally not life threatening but they are ____________
during spring, summer, & fall.
A. | beautiful | C. | scarce | B. | annoying | D. | pink |
|
|
|
65.
|
Which of the following is not a way to protect yourself from
wildlife?
A. | Stay calm | C. | Taunt a mother bear | B. | Wear proper clothing | D. | Use good
judgement |
|
|
|
66.
|
Which of the following is not a venomous snake in Georgia?
A. | Coral snake | C. | Timber rattler | B. | Indigo snake | D. | Cottonmouth |
|
|
|
67.
|
The only deadly spider(s) in the US is/are the
A. | Black Widow | C. | Tarantula | B. | Brown Recluse | D. | Both A & B |
|
|
|
68.
|
This snake has a white mouth and typically lives in aquatic areas.
A. | Timber rattler | C. | Coral snake | B. | Cottonmouth moccasin | D. | Copperhead |
|
|
|
69.
|
Which of the following diseases can be carried by ticks?
A. | Lyme disease | C. | Tularemia | B. | Rocky Mountain Spotted
Fever | D. | All of the
Above |
|
|
|
70.
|
What is the best way to protect yourself from the Saddleback Caterpillar?
A. | OFF Deep Woods Spray | C. | Long sleeved shirts | B. | Wear a tank top | D. | Carry a lucky rabbit’s
foot |
|
|
|
71.
|
DBH is a measurement of the diameter of a tree at breast height which is:
A. | 4 feet above the ground level | C. | 5 feet above ground level
| B. | 4.5 feet above ground level | D. | 5.5 feet above ground level
|
|
|
|
72.
|
An instrument consisiting of a thin wedge of glass that is used to determine the
number of trees that should be counted when determining the basal per acre is called what?
A. | dendrometer | C. | hyposmeter | B. | prism | D. | clinometer |
|
|
|
73.
|
You tally 12 trees using a 10 factor wedge prism. What is the sqaure feet of
basal area per acre of the treees around that point?
|
|
|
74.
|
______ species, sometimes called confiers, are trees that have leaves in the
form of needles.
A. | Hardwood | C. | Evergreen | B. | Softwood | D. | Deciduous |
|
|
|
75.
|
When measuring diameter breast height of a tree with a Biltmore Stick, how many
inches from the eye is the stick held?
A. | 21 inches | C. | 25 inches | B. | 24 inches | D. | 30 inches |
|
|
|
76.
|
The basal area is _____ if one has tallied 8 trees with a 10 factor prism.
A. | 8 sq. ft | C. | 800 sq. inches | B. | 80 sq. inches | D. | 80 sq. ft |
|
|
|
77.
|
The ability of soils to release water so that it flows through the topsoil into
the subsoil, and eventually to aquifers, is called _____.
A. | drainage | B. | weathering | C. | filtration | D. | aggregation |
|
|
|
78.
|
In which season do deer species rut?
A. | Autumn | B. | Spring | C. | Summer | D. | Winter |
|
|
|
79.
|
Trees cut for lumber are generally cut into _____ lengths.
|
|
|
80.
|
What is a Biltmore stick commonly used for?
A. | Measuring the harvestable height of a tree | B. | Clearing slash from
the forest floor | C. | Marking trees for culling | D. | Marking the ground to measure the level of pond
succession |
|
|
|
81.
|
A. | Sweetgum | C. | White Oak | B. | Sycamore | D. | Pecan |
|
|
|
82.
|
A. | Yellow-poplar | C. | Sugar Maple | B. | Red Maple | D. | Lodgepole Pine |
|
|
|
83.
|
 Needles 6-9 inches long Needles 6-9 inches longA. | Loblolly Pine | C. | Red Spruce | B. | Shortleaf Pine | D. | Black Cherry |
|
|
|
84.
|
 Needles 10-18 inches, bundles of
three A. | Longleaf Pine | C. | Lodgepole Pine | B. | Balsam Fir | D. | Elm |
|
|
|
85.
|
A. | Shortleaf Pine | C. | Sitka Spruce | B. | Eastern Redcedar | D. | American Beech |
|
|
|
86.
|
A. | American Beech | C. | Yellow-Poplar | B. | Black Cherry | D. | Red Pine |
|
|
|
87.
|
Using a 1 inch diameter class, a 15.2 inch tree will be tallied as what diameter
tree?
|
Multiple Response
Identify one
or more choices that best complete the statement or answer the question.
|
|
|
88.
|
Which of the following is a conifer?
|
|
|
89.
|
You are using a clinometer to determine tree height on level ground from a
distance of 100’. Your reading to the tops of the tree is +85%; the bottom reading is -5%. What
is the height of the tree?(NRS.02.03)
|
|
|
90.
|
What is the stinging bug found in our area that is not an insect?
|
|
|
91.
|
Which of the following would be an example of a topographic hazard?
|
|
|
92.
|
How many feet are usually in a “log”?
|
|
|
93.
|
To estimate the height of a tree use a(n) _______. (NRS.02.03)
|
|
|
94.
|
What does the black widow have on the underside of
its abdomen?
|
|
|
95.
|
Which of the venomous
snakes is solid black?
|
|
|
96.
|
What is a substance used to stop pain or
itching?
|
|
|
97.
|
What does DBH stand for?
|
True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
98.
|
A sandy beach is an example of Class I land.
|
|
|
99.
|
Timber stand improvement may include removing desirable trees for thinning
purposes.
|
|
|
100.
|
The sex of a deer can consistently be determined by the track.
|
|
|
101.
|
Only one buck uses a scrape, and does do not use scrapes.
|
|
|
102.
|
White-tailed deer have always been abundant throughout the last 200
years.
|
|
|
103.
|
White-tailed deer have a field of vision that is limited to 200 degrees.
|
|
|
104.
|
The only mechanism of touch that whitetails experience is from their hooves on
the ground.
|
|
|
105.
|
Almost all activity (80%) at scrape sites is during the night.
|
|
|
106.
|
All deer have the same home range size.
|
|
|
107.
|
When 12 to 18-month-old deer travel 1 to 3 miles away from their birth range to
establish an adult home-range, this is referred to as “dispersal.”
|
Matching
|
|
|
A. | Younger | F. | Rut | B. | Home Range | G. | Photoperiod | C. | Rub-urination | H. | Directional Hearing | D. | Bachelor Groups | I. | Fetal Scale | E. | Fawn Recruitment
Rate |
|
|
|
108.
|
The ___________ is the period of the year where active breeding in whitetails
is at the highest point.
|
|
|
109.
|
Whitetail bucks form ____________ during the summer months due to low
testosterone levels.
|
|
|
110.
|
One goal of Quality Deer Management is to minimize the harvest of
_______________ bucks.
|
|
|
111.
|
The casting of antlers is regulated by testosterone and ____________.
|
|
|
112.
|
The ability of whitetails to move their ears without moving their head is
referred to as ___________.
|
|
|
113.
|
When a buck places both tarsal glands together and urinates on them, this is
referred to as __________.
|
|
|
114.
|
The amount of fawns per doe that survive to become part of the huntable deer
herd every fall.
|
|
|
115.
|
The place where a deer will spend nearly 100% of their time
|
|
|
116.
|
Biologists will use a __________ to determine the timing of the rut during each
hunting season.
|
|
|
A. | drainage | E. | slope | B. | effective depth | F. | topsoil texture | C. | erosion | G. | topsoil thickness | D. | permeability |
|
|
|
117.
|
process of water being removed from the soil
|
|
|
118.
|
the proportion of sand, silt, and clay in the topsoil
|
|
|
119.
|
the surface layer of the land measured from ground level to the beginning of
the subsoil
|
|
|
120.
|
the steepness of the area or field
|
|
|
121.
|
the depth to which plant roots can easily penetrate
|
|
|
122.
|
ability of air and water to move through the subsoil
|
|
|
123.
|
the percentage of the original topsoil which has suffered the harmful effects
of water and wind
|